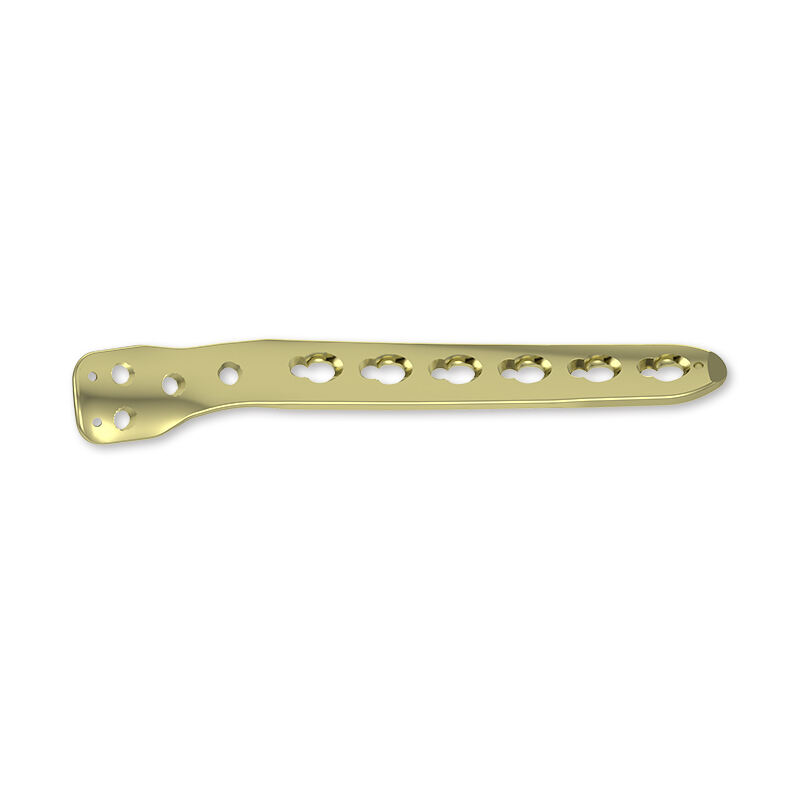
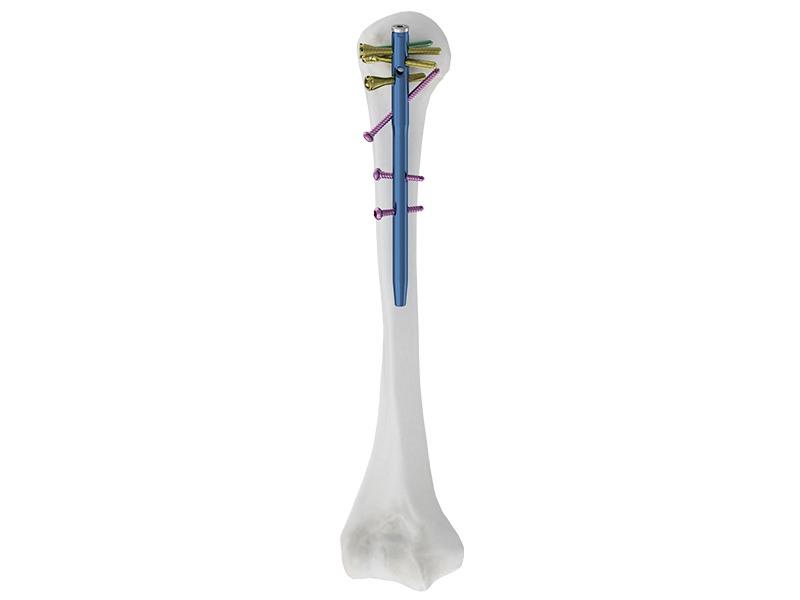
ортопедиялық фиксация құрылғылары
Ортопедиялық бекіту құрылғылары сынған немесе әлсіреген сүйектер мен буындарды тұрақтандыру және қалпына келтіру үшін арналған медициналық құралдар. Бұл құрылғылар әртүрлі формаларда болады, мысалы, пластиналар, таяқшалар, бұрандалар, сымдар және шегелер, әрқайсысының нақты мақсаты бар. Олардың негізгі функциялары емделу кезінде сүйектердің дұрыс орналасуын сақтау, сүйек displacement тәуекелін азайту және дененің салмағын қолдау болып табылады. Бұл құрылғылардың технологиялық ерекшеліктері остеоинтеграцияны ынталандыратын және инфекция тәуекелін азайтатын заманауи материалдарды, сондай-ақ минималды инвазивтілікті қамтамасыз ететін конструкцияларды қамтиды. Қолдану ауқымы сынулар мен остеотомияларды емдеуден бастап, омыртқа деформацияларын түзетуге және буын біріктірулерін қолдауға дейін созылады. Бұл құрылғылардың әмбебаптығы мен дәлдігі оларды заманауи ортопедиялық хирургияда алмастырылмайтын етеді.